What is HIV and AIDS?
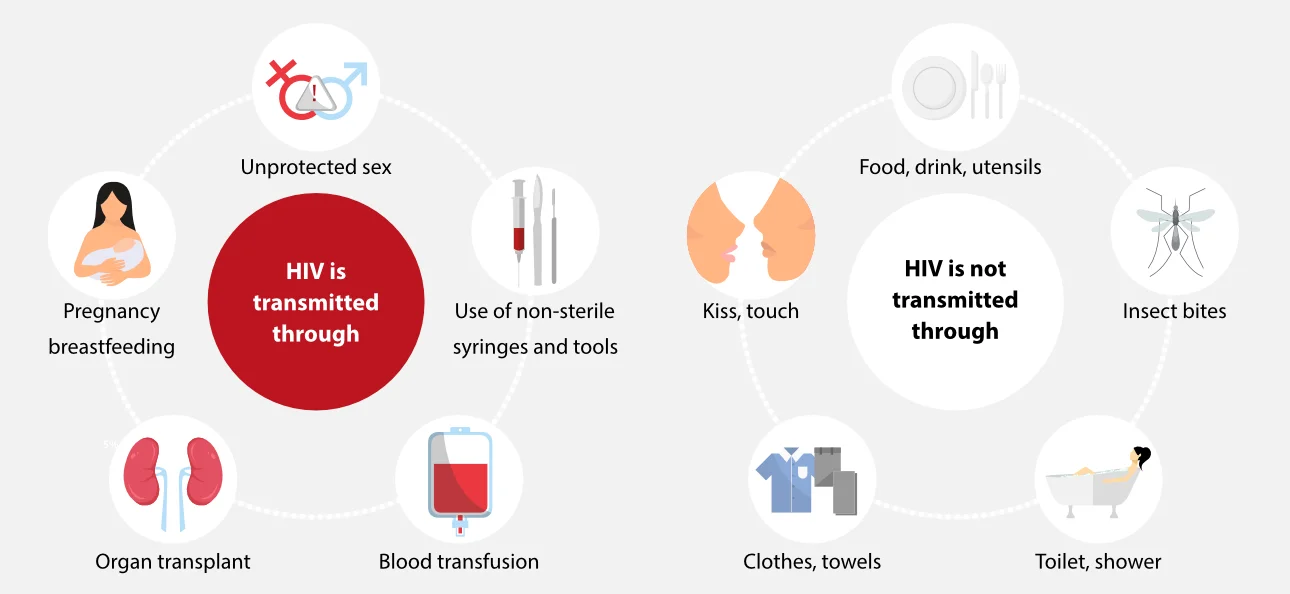
HIV is a virus that specifically targets the immune system, weakening the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases, leaving the infected person vulnerable to opportunistic infections and certain cancers. The virus can be transmitted through certain body fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection, occurring when the immune system is severely weakened, leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections and certain cancers.[1]
HIV prevalence
By the end of 2023, an estimated 39.9 million people were living with HIV globally, and an estimated 42.3 million people had died from HIV/AIDS-related complications. The African region is the most affected, with 1 in 30 adults (equivalent to approximately 3.41 TP3T) living with HIV, accounting for more than two-thirds of all people currently living with HIV worldwide.

Challenges in HIV screening
HIV can affect any individual, regardless of sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, gender, age, or geographic location. It is a major global health problem, characterized by a large number of infections and high mortality rates. The only way to definitively determine HIV status is through testing. However, public health systems around the world face significant challenges in accurately screening for HIV due to the risk of false positives.
Solving the challenge
To address the challenges posed by current HIV screening and confirmation methods, it is necessary to find alternative methods that balance sensitivity, specificity, and cost-effectiveness. In this study, the researchers evaluated the performance of a new, cost-effective screening method, the Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo assay, as an alternative to the widely recognized ARCHITECT® HIV Ag/Ab combo assay. In addition, they compared the performance of the Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo assay with the gold standard confirmation method, INNO-LIA™ HIV I/II. The evaluation also included an alternative reference method, PCR. The findings from this study are expected to provide valuable information to healthcare professionals to improve the efficiency of HIV screening procedures and diagnoses.
The study analyzed retrospective data from a large cohort of individuals screened for HIV at MC during 2022–2023 using the Architect-HIV assay. From this dataset, 195 samples were selected based on the similarities and differences between the ARCHITECT® HIV Ag/Ab combo assay and the gold standard confirmatory assay INNO-LIA™ HIV I/II. These samples included: positive cases by both methods, positive cases by the ARCHITECT® method only, indeterminate cases, and negative cases by both methods. All selected samples underwent retesting using the Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo assay, with positive results from the ARCHITECT® method further confirmed by PCR. This rigorous process comprehensively evaluated the accuracy of the Mindray CL-900i-HIV assay, focusing specifically on potentially false-positive samples, thereby providing strong evidence of its efficacy and feasibility as an alternative screening method.
Table 1. Comparison of Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo results with INNO-LIA™ HIVI/II confirmatory assay.
|
|
INNO-LIA-HIV+ |
INNO-LIA-HIV- |
INNO-LIA-HIV IND |
Total |
| CL-900i-HIV+ |
38 (20.5%) |
0 (0%) |
5 (2.7%) |
43 (23.2%) |
| CL-900i-HIV- |
0 (0%) |
121 (65.4%) |
21 (11.4%) |
142 (76.8%) |
| Total |
38 (20.5%) |
21 (65.4%) |
26 (14.1%) |
185 (100%) |
Table 2. Concordance assessment between Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo in comparison to INNOLIA™ HIVI/II (n = 159).
| Performance parameters |
|
| Sensitivity (%) |
100% (90.7-100) |
| Specificity (%) |
100% (97.0-100) |
| PPV (%) |
100% (90.7-100) |
| NPV (%) |
100% (97.0-100) |
| OPA (%) |
100% (97.7-100) |
| PPA (%) |
100% (90.7-100) |
| NPA (%) |
100% (97.0-100) |
| Efficiency/accuracy (%) |
100% (97.7-100) |
| Cohen's Kappa coefficient |
1.00 (1.00-1.00) |

The Mindray CL-900i-HIV Ag/Ab combo assay is a two-site CLIA sandwich assay. It uses monoclonal antibodies and HIV-1 or HIV-2 antigens coated on microparticles, allowing simultaneous testing of both antigens and antibodies associated with HIV infection. The procedure involves combining the sample with assay diluent and magnetic microparticles coated with HIV antigens and antibodies, then performing a chemiluminescence reaction and measuring the emitted light as relative light units (RLUs). This method demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity compared to the gold standard confirmatory method INNO-LIA™ HIV I/II, with no false positives noted.
References:
[1]. What Are HIV and AIDS? HIV. Gov. available from: What Are HIV and AIDS? | HIV.gov
[2]. HIV. The Global Health Observatory. World Health Organization. 2024.
Source: https://www.mindray.com/